Jump Training Injuries: Rethinking NBA Player Practices
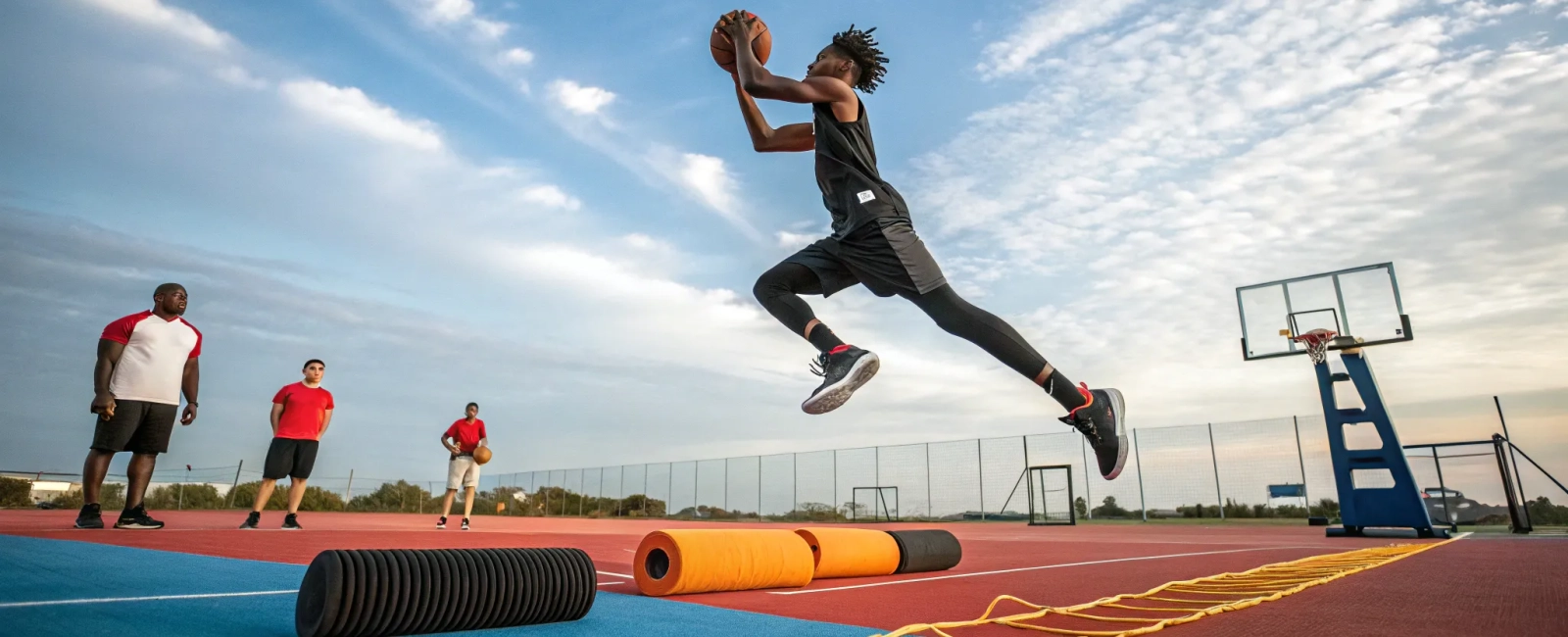

Jumping Into Success: How Young Athletes Can Avoid Overtraining and Boost Performance
There’s nothing quite like the rush of soaring through the air to make that game-winning shot or block. For aspiring athletes, especially those eyeing a future in basketball, mastering the art of jumping is crucial. But with the dream of reaching new heights comes the risk of injuries that can sideline even the most dedicated players. Let’s explore how rethinking training practices can help young athletes prevent overtraining injuries and enhance their performance on the court.
The Hidden Dangers of Overtraining
Pushing oneself to the limit is often seen as the hallmark of a committed athlete. The drive to excel and exceed personal bests can be a powerful motivator, fostering discipline and perseverance. However, there’s a fine line between training hard and overtraining. Recent studies have shown that excessive training loads, especially those involving high-intensity movements like jumping, can significantly increase the risk of injuries. Understanding where this line lies is essential for long-term athletic success.
For instance, a systematic review examining injury risks in basketball revealed that players who had fewer decelerations during games were more prone to injuries. Specifically, those who executed three or fewer decelerations at 2 m/s² per game faced a higher injury risk. This finding underscores the importance of not just the quantity of movements but also their quality and variability. Players who engage in more varied and controlled movements are better equipped to handle the physical demands of the game without succumbing to overuse injuries.
Additionally, covering less distance—1.3 miles or less per game—was linked to increased injuries. This suggests that not just intensity but also the variety and volume of movements play a role in keeping athletes safe. Engaging in a wider range of movements helps distribute physical stress more evenly across different muscle groups and joints, reducing the likelihood of overuse in any one area. Incorporating diverse training routines that mimic the dynamic nature of actual gameplay can thus be a strategic approach to injury prevention.
Moreover, mental fatigue often accompanies physical overtraining, leading to decreased focus and increased error rates during games and practices. This mental strain can further exacerbate the risk of injuries, as athletes may not execute movements with the necessary precision. Therefore, balancing training intensity with adequate rest is not only crucial for physical health but also for maintaining mental sharpness on the court.
The Mechanics of Safe Landing
Jumping isn’t just about the takeoff; how you land can make all the difference. Proper landing techniques are vital for minimizing impact forces and protecting the joints from injury. Improper landing techniques, such as letting the knees buckle inward (valgus position), can put enormous strain on the knees, leading to serious injuries like ACL and meniscus tears. These injuries not only cause significant pain and downtime but can also have long-term implications for an athlete’s career.
Orthopedic experts emphasize the importance of practicing proper landing mechanics from a young age. Working with coaches or physical therapists to hone these skills can help athletes develop muscle memory for safe movements. One key aspect is strengthening the muscles around the knees and hips to provide better support during high-impact actions. For example, incorporating exercises like lateral lunges and hip abductors can enhance the stability of the lower body, making it easier to maintain proper alignment during landings.
Additionally, proprioceptive training, which involves exercises that improve the body’s ability to sense its position in space, can play a significant role in safe landings. Activities such as balance board exercises or single-leg stands with eyes closed can enhance an athlete’s awareness of their body’s positioning, allowing for quicker and more accurate adjustments during dynamic movements.
Another critical component is the role of footwear and court surfaces in safe landings. Shoes that provide adequate cushioning and support can absorb some of the impacts from jumping and landing, reducing the stress on joints. Similarly, playing on surfaces that offer appropriate traction without being overly abrasive can help prevent slips and awkward landings that may lead to injuries.
Furthermore, incorporating video analysis into training sessions can provide visual feedback to athletes on their landing techniques. By reviewing footage of their jumps and landings, players can identify and correct flaws in their form, leading to more consistent and safer movements.
Building a Strong Foundation with Warm-Ups
A well-rounded warm-up routine is more than just a formality before the main event; it’s a critical component of injury prevention and performance enhancement. Proper warm-ups prepare the body for the physical demands of the sport, increase blood flow to muscles, and enhance neuromuscular efficiency. For young athletes, establishing effective warm-up habits early on can lay the groundwork for a healthier and more productive athletic career.
Incorporating exercises that focus on core stability, balance, and coordination can prepare the body for the demands of intense play. A strong core enhances overall stability, making it easier to execute complex movements with precision and reducing the risk of falls or twists that can lead to injuries. Balance exercises, such as single-leg stands or dynamic balance drills, improve the body’s ability to maintain equilibrium during rapid directional changes, common in basketball gameplay.
Starting with activities that raise the heart rate, like light jogging or jumping rope, helps to loosen the muscles and increase blood flow. This initial phase not only warms up the muscles but also primes the nervous system for the upcoming activity, enhancing reaction times and coordination. Transitioning into dynamic stretching—moving stretches that take joints through their full range of motion—can further prime the muscles and joints. Some effective dynamic stretches include leg swings, lunges with a twist, and arm circles, all of which mimic the movements performed during the game, ensuring that the muscles are prepared for the specific demands they will face.
According to guidance from EuroSafe, introducing balance training and neuromuscular exercises into warm-ups can significantly improve knee and ankle control. This is especially important for movements involving rapid changes in direction and explosive jumps. Incorporating drills like agility ladder exercises or cone drills can enhance an athlete’s ability to move quickly and efficiently, reducing the likelihood of awkward landings or sudden stops that may result in injuries.
Moreover, including sport-specific movements in the warm-up can enhance muscle memory and coordination, ensuring that athletes are not only physically prepared but also mentally ready to perform at their best. For example, mimicking the jumping and landing patterns of basketball can help athletes transition seamlessly from the warm-up to the game, maintaining optimal performance levels from the first whistle to the last.
Strength Training: More Than Just Muscle
While building muscle strength is often associated with bulking up, for young athletes, it’s about creating a resilient body capable of handling the stresses of their sport. Incorporating strength and power exercises into training routines can enhance performance and reduce injury risk. Strength training contributes to improved muscle balance, joint stability, and overall athleticism, which are crucial for maintaining peak performance throughout the season.
Focusing on muscle groups that support jumping and landing—such as the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and core—can offer better stability and control. Exercises like squats, deadlifts, and plyometric drills (which involve quick, powerful movements like box jumps or depth jumps) can be particularly beneficial. These exercises not only build strength but also enhance the power and explosiveness needed for effective jumping and rapid movements on the court.
Incorporating unilateral exercises, which work one limb at a time, can address muscle imbalances and improve overall coordination. For example, single-leg deadlifts or single-leg squats can help identify and correct asymmetries in strength and stability, ensuring that both sides of the body are equally prepared for the demands of the game.
Additionally, integrating flexibility training into strength routines can enhance muscle elasticity and joint mobility, further reducing the risk of strains and sprains. Dynamic strength training, which combines strength and movement, can simulate the actual conditions of the game, making the training more functional and relevant to performance.
However, it’s important to balance strength training with adequate rest and recovery. Overloading muscles without sufficient downtime can lead to fatigue, which is another risk factor for injuries. Fatigue impairs muscle function and coordination, increasing the likelihood of improper movements and accidents during games and practices. Therefore, scheduling regular rest days and varying the intensity of workouts can help prevent overtraining and ensure that muscles have ample time to recover and adapt.
Paying attention to the body’s signals and allowing for recovery days can help maintain peak performance levels. Incorporating active recovery techniques, such as light stretching, yoga, or low-intensity swimming, can promote muscle relaxation and reduce soreness without adding additional stress to the body.
Balancing Act: Training Load and Recovery
The enthusiasm to improve can sometimes lead athletes to increase their training load too quickly. Rapid changes in training intensity or duration can put undue stress on the body, leading to overuse injuries and burnout. Monitoring training loads and making gradual adjustments is crucial for maintaining a healthy balance between improvement and injury prevention.
One approach is to keep track of perceived exertion levels during training sessions. This means noting how hard an exercise feels on a scale from easy to extremely hard. By correlating these perceptions with actual performance metrics, athletes can find a sweet spot where they’re challenging themselves without overdoing it. Tools like training logs or mobile apps can assist in tracking these metrics, providing valuable insights into an athlete’s progress and recovery needs.
Additionally, periodization—structuring training programs in cycles that alternate between different intensities and focuses—can help manage training loads effectively. By planning phases of intense training followed by lighter periods or active recovery, athletes can continuously improve while minimizing the risk of overtraining. This strategic approach ensures that the body has time to adapt and strengthen, enhancing overall performance and resilience.
Research has shown that the number of minutes played in games preceding an injury is often higher. This suggests that cumulative fatigue can increase injury risk. Ensuring that players have adequate rest between games and practices can mitigate this risk. Implementing policies that limit the number of games or practices within a certain timeframe can help manage overall training loads and prevent excessive fatigue.
Furthermore, incorporating flexibility in training schedules to accommodate unexpected increases in load—such as during playoff seasons or intensive training camps—can help athletes maintain their performance without compromising their health. Flexibility allows for adjustments based on how the body is responding, ensuring that training remains effective without pushing beyond safe limits.
In addition to physical rest, mental recovery is equally important. High levels of stress and mental fatigue can negatively impact an athlete’s focus and motivation, contributing to decreased performance and increased injury risk. Practices such as mindfulness meditation, adequate sleep, and relaxation techniques can support mental recovery, enhancing overall well-being and athletic performance.
Taking Care of Your Knees: A Priority
The knees are among the most vulnerable joints for basketball players due to the constant jumping, landing, and quick directional changes. Implementing specific exercises to strengthen and stabilize the knees can go a long way in preventing injuries. Proactive knee care involves a combination of strengthening, mobility, and stabilization exercises tailored to the demands of the sport.
Incorporating movements that focus on joint mobility can improve flexibility and reduce stiffness. Dynamic stretching and range-of-motion exercises before activities can keep the joints supple and ready for action. After workouts, static stretching can help maintain muscle length and joint health, reducing the likelihood of tightness that can lead to injury.
Foam rolling is another technique that can alleviate muscle tension and aid in recovery. Regular use of a foam roller on the thighs, calves, and hips can enhance blood flow, reduce muscle soreness, and improve overall mobility. This self-myofascial release technique helps break down scar tissue and knots in the muscles, promoting better movement patterns and reducing the strain on the knees.
A knee-strengthening program might include exercises like step-ups, hamstring curls, and balance drills. Step-ups help build functional strength in the legs, mimicking the movements of stepping onto platforms or during jumps. Hamstring curls target the muscles at the back of the thighs, providing crucial support to the knee joint and preventing imbalances that can lead to injuries.
Balance drills, such as single-leg stands on unstable surfaces like balance boards or BOSU balls, enhance proprioception and neuromuscular control. Improved balance reduces the risk of awkward landings and sudden twists that can compromise knee stability. Additionally, incorporating resistance bands into knee exercises can provide incremental challenges, further strengthening the stabilizing muscles around the joint.
Addressing muscle imbalances is key, as asymmetries can lead to improper movement patterns and increased injury risk. Regular assessments by sports physiotherapists can help identify any imbalances in strength or flexibility, allowing for targeted interventions. Correcting these imbalances through tailored exercises ensures that both sides of the body are equally prepared to handle the demands of the sport, promoting overall knee health and function.
Moreover, educating young athletes on the importance of listening to their bodies and recognizing the early signs of knee strain can prevent minor issues from escalating into serious injuries. Encouraging open communication with coaches and medical professionals fosters a supportive environment where players feel empowered to seek help when needed.
The Role of Endurance in Injury Prevention
As the game progresses, fatigue sets in, and the likelihood of improper movements increases. Fatigue not only diminishes physical performance but also impairs cognitive functions such as decision-making and reaction times. Working on cardiovascular endurance can help athletes maintain proper form throughout the game, reducing the risk of injuries associated with tiredness and reduced coordination.
Incorporating interval training—alternating periods of high-intensity effort with low-intensity recovery—can improve both aerobic and anaerobic fitness. This type of training replicates the stop-and-go nature of basketball, where bursts of intense activity are followed by brief moments of rest. Enhancing both energy systems ensures that athletes can sustain high levels of performance without experiencing debilitating fatigue.
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) has been shown to be particularly effective in boosting cardiovascular endurance while also promoting muscle strength and agility. For example, sprinting for 30 seconds followed by a minute of light jogging or walking can significantly enhance an athlete’s ability to recover quickly between intense plays, maintaining performance levels throughout the game.
Steady-state cardio, such as long-distance running or cycling at a consistent pace, also plays a role in building a strong aerobic base. A well-developed aerobic system allows athletes to recover more efficiently between high-intensity efforts, delaying the onset of fatigue and maintaining higher performance levels during critical moments of the game.
Moreover, incorporating sport-specific endurance drills can provide additional benefits. Drills that mimic the movements and pace of basketball, such as shuttle runs, defensive slides, and continuous jumping, can enhance both endurance and sport-specific skills. This integration ensures that endurance training directly translates to improved on-court performance.
Proper hydration and nutrition are also integral to maintaining endurance and preventing fatigue-related injuries. Ensuring that athletes consume adequate fluids, electrolytes, and balanced meals supports energy production and muscle function, enabling them to perform at their best for longer periods.
Additionally, focusing on recovery strategies, such as active recovery days and adequate sleep, supports the body’s ability to repair and replenish energy stores. This holistic approach to endurance training ensures that athletes are not only building stamina but also maintaining overall health and readiness for competition.
Starting Early: The Advantage of Youth
Introducing these practices at a young age can set the foundation for a long, healthy athletic career. Early exposure to proper training techniques and injury prevention strategies ensures that athletes develop good habits that will benefit them throughout their sporting journey. Learning proper techniques and building strength before bad habits form makes it easier to progress without setbacks, fostering a sustainable approach to athletic development.
Programs designed for younger athletes should focus on fundamentals, making training both effective and enjoyable. Emphasizing the joy of movement and the satisfaction of mastering new skills can cultivate a lifelong love for the sport. Incorporating games and playful drills into training sessions can keep young athletes engaged and motivated, reducing the risk of burnout and fostering a positive association with physical activity.
Encouraging a positive attitude toward injury prevention can foster long-term commitment to safe practices. Educating young athletes about the importance of listening to their bodies, recognizing signs of overtraining, and prioritizing rest creates a mindset that values health alongside performance. This balanced approach ensures that athletes are not only focused on immediate gains but also on their long-term well-being and success.
Mentorship from experienced coaches and older athletes can also play a crucial role in instilling these values. By modeling good practices and sharing personal experiences, mentors can inspire young athletes to adopt effective training habits and prioritize their health. Creating a supportive and knowledgeable coaching environment encourages open communication and proactive management of training loads and injury prevention measures.
Moreover, integrating cross-training into youth programs can enhance overall athleticism and reduce the risk of overuse injuries. Participating in a variety of sports and activities develops a broader range of physical skills and reduces the repetitive strain associated with specializing too early in one sport. This diverse training approach contributes to a more balanced and resilient athletic foundation, supporting long-term performance and health.
Additionally, fostering a community-oriented approach to youth sports can provide emotional and psychological support, further enhancing an athlete’s commitment to safe and effective training practices. Encouraging teamwork, mutual respect, and collective responsibility creates an environment where athletes look out for one another, promoting a culture of safety and mutual care.
Final Thoughts
The path to becoming a top-tier athlete isn’t just about pushing harder and jumping higher; it’s about training smarter. By understanding the risks associated with overtraining and improper techniques, young athletes can take proactive steps to protect themselves. This comprehensive approach not only enhances performance but also ensures that athletes can enjoy a long and healthy career in their chosen sport.
Implementing proper warm-up routines, focusing on strength and balance, and respecting the body’s need for recovery are all essential strategies. Each of these components plays a critical role in building a resilient and capable athlete, ready to face the challenges of competitive sports without succumbing to preventable injuries. Moreover, fostering a positive and informed attitude toward training and injury prevention empowers athletes to make decisions that support their long-term goals and well-being.
With the right approach, jumping can remain a source of joy and achievement, propelling athletes to new heights without the setback of preventable injuries. Emphasizing quality training, balanced workloads, and comprehensive physical care ensures that young athletes not only reach their immediate performance goals but also build a sustainable foundation for future success. By prioritizing smart training practices, young athletes can navigate the demanding world of sports with confidence, resilience, and the sustained enthusiasm necessary to excel both on and off the court.